Attraction #5 Towards carbon neutrality
Utilizing abundant renewable energy resources such as geothermal, small hydropower, and biomass
Utilizing abundant renewable energy resources such as geothermal, small hydropower, and biomass
Oita Prefecture has diverse and abundant energy resources, including geothermal and hot spring heat, which boasts Japan's largest power generation scale, number of sources, and output, small hydropower that utilizes agricultural waterways, which has the highest potential in Kyushu, and biomass that utilizes abundant forest resources.
According to the Permanent Zone 2022 Report, a joint report by Chiba University Kurasaka Laboratory (Professor Hidefumi Kurasaka, Faculty of Law, Politics and Economics, Chiba University) and the NPO Environmental Energy Policy Research Institute, the prefecture's renewable energy self-sufficiency rate is ranked second in the nation.
In particular, geothermal power generation and the use of geothermal (hot spring heat) account for more than 30% of the total supply, such as the Kyushu Electric Power Co., Ltd. Hatchobaru Geothermal Power Plant (Konoe Town), which boasts the largest amount of power generation in Japan, and the use of hot spring heat that is routinely used in households in places such as Beppu City.

Kyushu Electric Power Co., Inc. Hatchobaru Power Plant

Green Power Generation Oita Co., Ltd. Amase Power Plant

Johara Iji Small Hydroelectric Power Plant
Efforts toward local production and consumption of hydrogen (building an Oita hydrogen supply chain)
Hydrogen production demonstration project using renewable energy
In Kokonoe Town, Oita Prefecture, Obayashi Corporation (headquarters: Tokyo) began operation of a green hydrogen production demonstration plant that utilizes geothermal power generation in July 2021. The produced green hydrogen is transported to hydrogen stations within and outside the prefecture, as well as fuel for hydrogen engine vehicles, demonstration operations of marine fuel cell systems, and testing and research institutes outside the prefecture for actual use.
Furthermore, in Kokonoe Town, Oita Prefecture, Shimizu Corporation (headquarters: Tokyo) was selected for the Ministry of the Environment's project (Technology Development and Demonstration Project to Strengthen Guided Measures to Reduce CO2 Emissions), and a demonstration project was conducted in FY2020 to produce low-cost green hydrogen using Oita Prefecture's abundant geothermal energy and woody biomass made from abundant forest resources. In the future, hydrogen production on a commercial scale is expected.

Obayashi Corporation Green Hydrogen Production Demonstration Plant
Establishment of the Oita Prefecture Energy Industry Business Association “Hydrogen-related Industry Subcommittee”
In June 2021, we established the "Hydrogen-related Industries Subcommittee" at the Oita Prefecture Energy Industry Association (secretariat: Oita Prefecture Commerce, Tourism and Labor Department, New Industry Promotion Office) in order to take advantage of Oita Prefecture's hydrogen potential and promote initiatives to develop related industries, from hydrogen supply to utilization. In addition to disseminating information on hydrogen and holding seminars, we aim to match participating companies and create business.
Companies in the prefecture are conducting research and development on hydrogen production from silicon-containing waste generated from the semiconductor industry and other industries, hydrogen production through the thermal decomposition of coal, and research aimed at introducing ocean-going ships that use hydrogen as fuel. In addition, consideration of new uses for hydrogen produced within the prefecture is progressing, and efforts to build a hydrogen supply chain for Oita Prefecture are accelerating.

Scene from the hydrogen-related industry subcommittee
Enhancing support systems related to hydrogen
The Oita Prefecture Energy Industry Business Association has established a subsidy system (Eco Energy Challenge Support Project) for research and development and demonstration tests related to hydrogen, etc., and supports the challenging business development of member companies.
Additionally, the prefecture has established a subsidy system for the construction of hydrogen stations and the introduction of fuel cell vehicles and fuel cell forklifts, which can be used in conjunction with national and municipal subsidy systems.

Shimizu Corporation Hydrogen Production Demonstration Commencement Ceremony
Efforts to realize “Green Industrial Complex Oita”
Formulation of the “Green Industrial Complex Oita Promotion Plan”
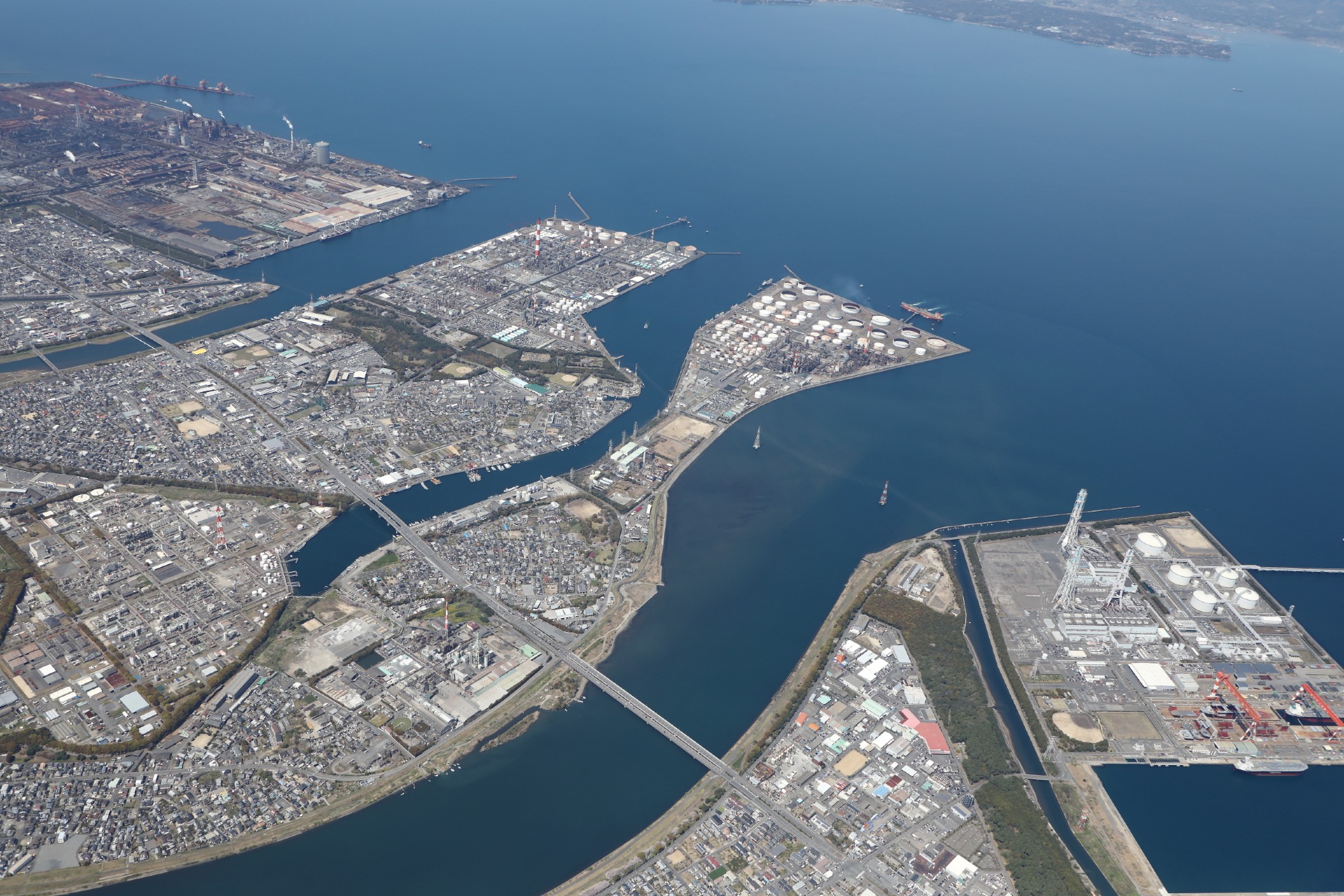
The prefecture is home to basic material industries such as steel, petrochemicals, lime, and cement, which support the Japanese economy.However, the prefecture ranks 13th in the country in terms of CO2 emissions (the prefecture ranks first in per capita emissions), and reducing emissions is an urgent issue. The Oita Industrial Complex is home to a diverse group of companies, including Kyushu's only oil refinery and Kyushu's largest LNG power plant, and the value of manufactured products shipped in 2019 was approximately 2 trillion yen, accounting for 46% of the prefecture's total. Therefore, achieving both carbon neutrality and sustainable growth is one of the most important issues for the development of the prefecture.
For this reason, the "Green Industrial Complex Oita" Promotion Council, an industry-academia-government collaboration, has compiled a vision for transformation with an eye toward 2050 as the "Green Industrial Complex Oita Promotion Concept" shared by all concerned parties. We will continue to steadily advance our efforts to achieve this goal.


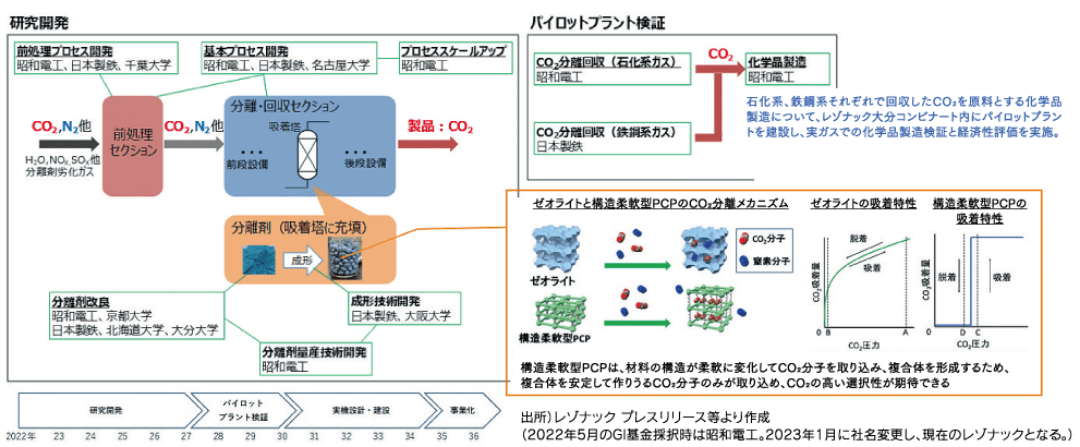
Resonac and Nippon Steel collaborate with six national universities to begin development of separation and recovery technology for low-concentration CO2 contained in factory exhaust gas.
A joint project between Resonac Co., Ltd., Nippon Steel Corporation, and six national universities (Oita University, Osaka University, Kyoto University, Chiba University, Nagoya University, and Hokkaido University) is the National The technology was selected for the Green Innovation Fund Project by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), and full-scale technology development began in October 2022.
This project uses technology possessed by both parties and the university to efficiently separate and recover CO2 from low-pressure, low-concentration (atmospheric pressure, CO2 concentration 10% or less) exhaust gas.The project aims to realize revolutionary low-cost technology and implement it in society in the late 2030s. Furthermore, Resonac aims to build a business model that reuses and sells the recovered CO2 as a raw material for chemical products.